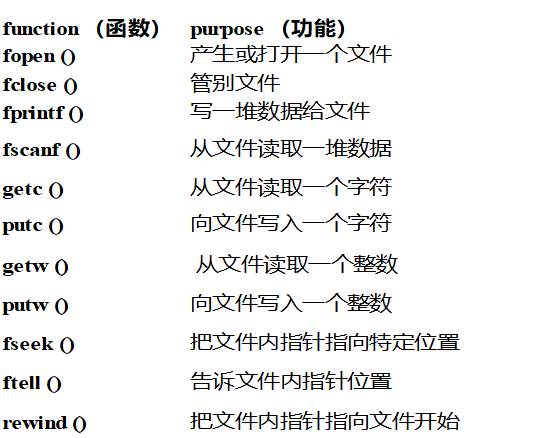
文件可用于存储大量持久性数据。 与许多其他语言一样,“ C”提供了以下文件管理功能,
- 创建文件;
- 打开文件;
- 读取文件;
- 写入文件;
- 关闭文件
例1.利用fseek函数读取数据
如果一个文件中有很多记录,并且需要访问特定位置的记录,则需要遍历它之前的所有记录以获取记录。
这会浪费大量的内存和操作时间。使用 fseek() 可以更轻松地获取所需数据。
顾名思义,fseek() 将光标定位到文件中的给定记录。
fseek语法:
|
1 |
fseek(FILE * stream, long int offset, int whence); |
第一个参数流是指向文件的指针。第二个参数是要查找的记录的位置,第三个参数指定偏移开始的位置:
| Whence | Meaning |
|---|---|
SEEK_SET |
Starts the offset from the beginning of the file. |
SEEK_END |
Starts the offset from the end of the file. |
SEEK_CUR |
Starts the offset from the current location of the cursor in the file. |
例1.fseek函数的应用
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct threeNum
{
int n1, n2, n3;
};
int main()
{
int n;
struct threeNum num;
FILE *fptr;
if ((fptr = fopen("C:\\program.bin","rb")) == NULL){
printf("Error! opening file");
// Program exits if the file pointer returns NULL.
exit(1);
}
// Moves the cursor to the end of the file
fseek(fptr, -sizeof(struct threeNum), SEEK_END);
for(n = 1; n < 5; ++n)
{
fread(&num, sizeof(struct threeNum), 1, fptr);
printf("n1: %d\tn2: %d\tn3: %d\n", num.n1, num.n2, num.n3);
fseek(fptr, -2*sizeof(struct threeNum), SEEK_CUR);
}
fclose(fptr);
return 0;
}
该程序将以相反的顺序(从后到前)开始从文件 program.bin 中读取记录并打印出来。
除教程外,本网站大部分文章来自互联网,如果有内容冒犯到你,请联系我们删除!
